How Long Does Meth Stay in Your System? Everything You Should Know

- Meth is a highly addictive stimulant drug that affects the central nervous system. Its effects are felt almost immediately as it crosses the blood-brain barrier quickly.
- Depending on what type of drug test is used and how your body processes meth, it can be detected in your body for 1-3 days with most tests and up to 6 months with hair follicle tests.
- Meth use can have dangerous and life-threatening side effects such as heart attack, seizure, stroke, and coma.
- It can be difficult to stop using meth as its withdrawal symptoms can be severe and last for a long time.
How long meth stays in your system can vary from person to person, depending on how it was taken and how many repeated doses were taken. On average, meth can be detected in your system for 1-3 days; however, using hair follicle tests, it can be detectable for months. While meth may no longer be detectable in your system, the withdrawal effects can be felt for up to a year after last use.
What is Meth?
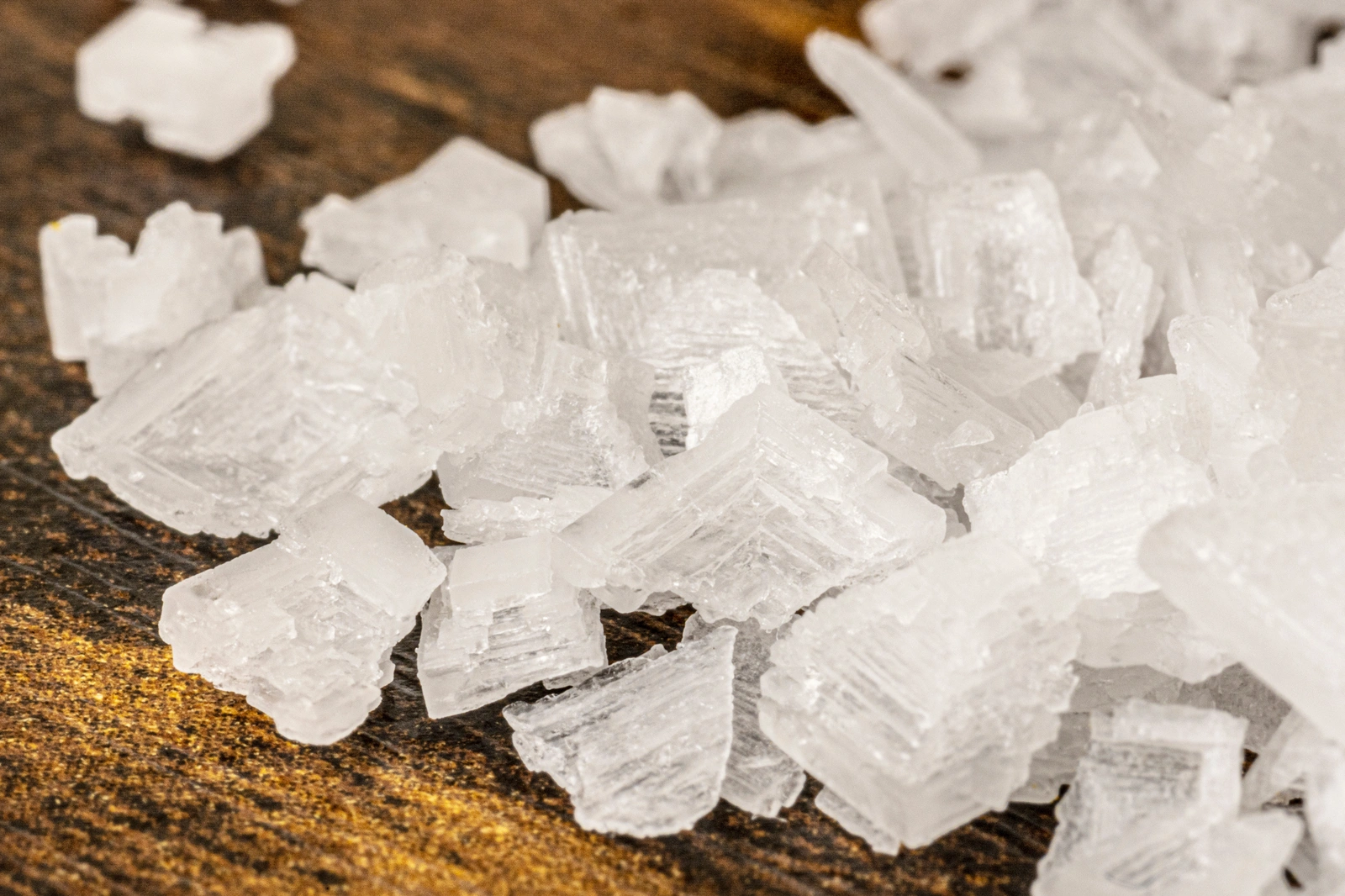
Methamphetamine is a strong, highly addictive stimulant drug that affects the central nervous system.[1] It is an odorless but bitter-tasting white crystal-like powder. It is easily dissolved in liquids, including alcohol. It can be smoked, snorted, taken orally, or injected. Street names for methamphetamine include meth, crystal meth, crank, speed, glass, tweak, chalk, Tina, and ice. [2]
Meth is derived from amphetamine which was originally intended as a nasal decongestant and bronchial inhaler. Meth is a much stronger stimulant than amphetamine, which means much more enters the brain, lasts longer, and has more negative effects on the central nervous system when compared to amphetamine.[3]
Meth affects the central nervous system (CNS) by increasing the release of neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. [4] Because meth is highly lipid-soluble, it crosses the blood-brain barrier quickly and can have an immediate effect on the CNS.
Dangerous side effects of meth include:[5]
- Agitation
- Chest pain
- Heart attack
- Irregular or stopped heartbeat
- Difficulty breathing
- Very high body temperature
- Kidney damage and possibly kidney failure
- Paranoia
- Seizures
- Severe stomach pain
- Stroke
- Coma
How Long Can Meth Be Detected In Your System?
Meth can be detected in your system for one day to six months. This is dependent on the drug test used, your frequency of use, the amount of meth you have used, and how quickly your body metabolizes and eliminates meth.
How long does meth stay in urine?
Methamphetamine can be detected in your urine for one to three days after you have taken it.[6]
About 70% of a meth dose is excreted in the urine in the first 24 hours. Methamphetamine does have a long urinary half-life of 25 hours and accumulates with repeated use.[7] For example, meth has been detected in urine seven days after taking four daily 10 mg doses.
While urine tests are cost-effective, the drawback of them is people have found ways to cheat on them and have a negative urine test even though they have used meth in the past few days.
How long does meth stay in the blood?
Generally, how long meth can be detected in blood is ten hours.[8] This can change based on the person and the method they use to consume meth. A 10 mg dose of meth taken intravenously is detected for 36-48 hours. If the meth is taken orally, it can be detected in blood for 24 hours.
Blood tests are more invasive and expensive, but they are more accurate as it is hard to cheat a blood test.
How long does meth stay in saliva?
Methamphetamine use can be detected in saliva for one to three days afterward.[9]
Saliva tests are more invasive but are less likely to be cheated on.
How long does meth stay in hair?
Hair provides a longer detection window for any substance than other drug tests. If you have been a chronic methamphetamine user, a hair follicle test can detect meth use for up to six months after last use. [10] If you have not been a chronic user, detection drops off between 90-120 days.
Hair follicle tests are more expensive but are capable of testing for meth use over a longer length of time.
How Long Do The Effects of Meth Last?
If methamphetamine is taken orally, peak concentrations occur in two to four hours. If meth is snorted, smoked, or injected, peak concentration happens within minutes. Methamphetamine elimination half-life ranges between six and fifteen hours.[11]
People feel an intense short rush for five to thirty minutes after using meth. They also have an increased energy level, decreased appetite, and a feeling of euphoria for six to twelve hours.
Meth Withdrawal
Abruptly stopping meth after long-term use can cause significant withdrawal symptoms, including:[12]
- Dysphoric mood
- Fatigue
- Vivid and unpleasant dreams
- Insomnia or hypersomnia
- Increased appetite
- Psychomotor retardation or agitation.
The methamphetamine withdrawal timeline starts with a crash phase, which happens in the first 12-24 hours and is characterized by exhaustion and fatigue. It is followed by a withdrawal phase that lasts 2-4 weeks but usually peaks in seven days. Finally, there can be a protracted extinction phase that lasts 6-12 months and is characterized by cognitive impairments and affective symptoms.[13] Withdrawal symptoms can be severe and cause so much discomfort that it is preferable to relapse. Providing behavioral and physical health support to the person going through withdrawal is important to prevent relapse and maintain sobriety.
Eliminating Meth From Your System
The only way to fully eliminate meth from your system is to stop using meth. It can be overwhelming and feel impossible to stop using meth. If you or a loved one want to stop using meth, there are options available. Meth addiction can be hard to stop on your own. Meth addiction treatment programs can help support you through your withdrawal symptoms and provide you with the tools to maintain sobriety. Treatment options include detox, inpatient, and outpatient programs which can be individualized to meet your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Long Meth Stays in Your System
Are you or a loved one struggling with Methamphetamine use?